DNA is a double stranded molecule made of 4 bases, adenine, cytosine, thymine and guanine. The bases are arranged so that adenine and cytosine match up and thymine and guanine match up
A-T
C-G
A single strand of DNA is represented with the letters of the bases for example
TACAATACT
The other strand will be the reverse. Like so. . .
TACAATACT
ATGTTATGA complementary
The order of the bases contains all of the information necessary to make proteins. This information is the genetic code. Think of the DNA as the master copy or set of instructions. When a protein is needed, a copy of the DNA must be made first. This process is called transcription. The RNA polymorace along with several other helpers reads the DNA strand and produces the RNA template.
Transcription DNA----->RNA
The DNA is not changed but a temporary copy is made.
RNA is similar to DNA but it is different in that it is less stable and single stranded. It also uses a uricil base instead of thymine from our example above the RNA polymorace would read one strand and put the bases in place for the RNA transcript
TACAATACT DNA Strand
AUGUUAUGA RNA Template
Notice that all of the Ts in the RNA strands have been replaced by Us. This is because RNA uses Uricil instead of Tymine.
After the RNA transcript is produced through transcription The Ribosome reads through the process called translation. The ribosome reads the RNA transcript and places one amino acid for every 3 bases, these 3 base groups may be referred to as triplets. The following is a chart of the amino acids that correspond to each triplet. These are called also called codons.
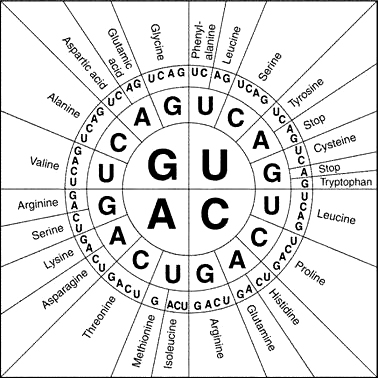
The amino acids are the building blocks of the protein. In our example sequence there are 3 triplets
AUGUUAUGA
AUG - Methionine
UUA - Leucine
UGA - Stop
This is a simple example but it demonstrates how the code is read. The order of the amino acids will eventually determine the function of the protein by changing its shape and structure.
This is a very simple explanation but it should give you the idea.